Created by Štejfová Kateřina
= VOC = eg. methane
Volatile organic compounds are compounds that have a high vapor pressure and low water solubility. Many VOCs are human-made chemicals that are used and produced in the manufacture of paints, pharmaceuticals, and refrigerants. ... Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are emitted as gases from certain solids or liquids.
Breathing VOCs can irritate the eyes, nose and throat, can cause difficulty breathing and nausea, and can damage the central nervous system as well as other organs. Some VOCs can cause cancer.
Human beings emit many volatile organic compounds (VOCs) of both endogenous (internally produced) and exogenous (external source) origin.
Toxic metals are harmful to humans and other organisms even at low concentration. Water-soluble toxic metals include arsenic, cadmium, lead, mercury, barium, chromium and silver. Some, such as arsenic, cadmium, lead and mercury, are particularly hazardous.
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) (oxid uhelnatý) is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom. It is a key ingredient in many processes in industrial chemistry.
Thermal combustion is the most common source of carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is an important in the production of many compounds ranging from drugs, fragrances, and fuels. It is produced by many organisms, including humans. Upon emission into the atmosphere, carbon monoxide may have roles potentially affecting climate change.
Carbon monoxide is harmful when breathed because it displaces oxygen in the blood and deprives the heart, brain and other vital organs of oxygen. Large amounts of CO can overcome you in minutes without warning — causing you to lose consciousness and suffocate.
PM stands for particulate matter (also called particle pollution - polétavý prach): the term for a mixture of solid particles and liquid droplets found in the air. Some particles, such as dust, dirt, soot, or smoke, are large or dark enough to be seen with the naked eye.
Exposure to such particles can affect both your lungs and your heart. Numerous scientific studies have linked particle pollution exposure to a variety of problems, including: ... decreased lung function. increased respiratory symptoms, such as irritation of the airways, coughing or difficulty breathing.
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) are fully or partly halogenated hydrocarbons that contain only carbon (C), hydrogen (H), chlorine (Cl), and fluorine (F), produced as volatile derivatives of methane, ethane, and propane. They are also commonly known by the brand name Freons.
In atmospheric chemistry, NO x is a generic term for the nitrogen oxides (oxidy dusíku) that are most relevant for air pollution, namely nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO 2 ). These gases contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, as well as affecting tropospheric ozone.
NO x gases are usually produced from the reaction among nitrogen and oxygen during combustion of fuels in air; especially at high temperatures, such as in car engines. In areas of high motor vehicle traffic, such as in large cities, the nitrogen oxides emitted can be a significant source of air pollution. NO x gases are also produced naturally by lightning.
nuclear explosions, radioactive decay of radon
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay (𝛼-decay), beta decay (𝛽-decay), and gamma decay (𝛾-decay).
https://www.cdc.gov/nceh/radiation/emergencies/healtheffects.htm
Sulfur dioxide or sulphur dioxide (oxid siřičitý) is the chemical compound with the formula SO2. It is a toxic gas responsible for the smell of burnt matches.
Although its chief uses are in the preparation of sulfuric acid, sulfur trioxide, and sulfites, sulfur dioxide also is used as a disinfectant, a refrigerant, a reducing agent, a bleach, and a food preservative, especially in dried fruits.
Sulfur dioxide causes a range of harmful effects on the lungs, as the EPA's most recent review of the science concluded: Wheezing (wheeze - sípat), shortness of breath and chest tightness and other problems, especially during exercise or physical activity.
are substances that are meant to control pests (škůdce). The term pesticide includes all of the following: herbicides, insecticides, termiticides, rodenticide, bactericide, insect or animal repellent, fungicide etc.
Carbon Dioxide or CO2 is a greenhouse gas that is natural and harmless in small quantities, but as levels rise it can affect productivity and sleep. Most commonly produced indoors by the air we exhale, CO2 levels concentrate indoors with less ventilation.
Carbon dioxide is a gas consisting of one part carbon and two parts oxygen. It is one of the most important gases on the earth because plants use it to produce carbohydrates [ˌkɑːbəʊˈhaɪdreɪt] in a process called photosynthesis. Since humans and animals depend on plants for food, photosynthesis is necessary for the survival of life on earth.
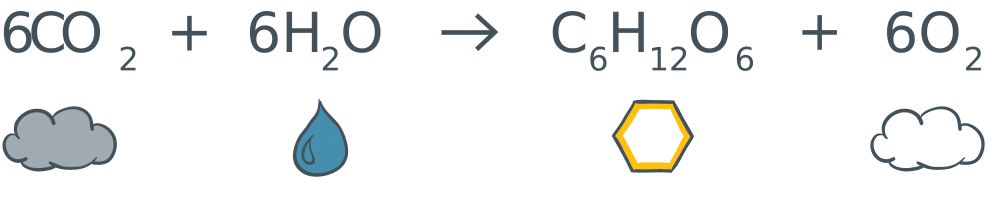
You have probably heard of CO2 emissions in the news regarding global warming. As CO2 builds up in our atmosphere from burning fossil fuels, it has a warming effect that could change the earth’s climate.
Indoor carbon dioxide concentrations are driven by a combination of outdoor CO2, indoor breathing and the ventilation rate of the building. As buildings and homes become more energy-efficient and airtight, this means we have less fresh air.
toxic waste, chemical waste material capable of causing death or injury to life. ... Waste containing dangerous pathogens, such as used syringes, is sometimes considered to be toxic waste. Poisoning occurs when toxic waste is ingested, inhaled, or absorbed by the skin.
The major physical impacts of a rise in sea level include erosion of beaches, inundation of deltas as well as flooding and loss of many marshes and wetlands.
gasoline that has not been treated with a lead compound.
Most skin cancers are caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. When you don't protect your skin, UV rays from sunlight or tanning beds can damage your skin's DNA. When the DNA is altered, it can't properly control skin cell growth, leading to cancer. A number of things can raise your chances of getting it. Always use sun block (sunscreen)!!!
There are five major renewable energy sources
Alternative forms of transportation to work include walking/biking, public transportation, hybrid vehicle travel, and carpooling (spolujízda).
Means of transport in future:
hyperloop (using magnetic technology)
transport capsules
MAAS - combining public and private transport
AV - electric autonomous vehicles
energy-saving bulbs
Climate change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may be natural, such as through variations in the solar cycle. But since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to burning fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas.
These phenomena include the increased temperature trends described by global warming, but also encompass changes such as sea-level rise; ice mass loss in Greenland, Antarctica (ice caps), the Arctic and mountain glaciers worldwide; shifts in flower/plant blooming; and extreme weather events (floods, deserts, hurricanes, drought [draʊt] (withering plants) → famine) .
Slow food: food which is carefully prepared using traditional cooking methods and organic ingredients, and is intended to be eaten and enjoyed slowly for maximum benefit.
Slow fashion: involves local artisans (řemeslník) and the use of eco-friendly materials, with the goal of preserving crafts and the environment and, ultimately, provide value to both consumers and producers. SF belongs to sustainable solutions, based on the repositioning of strategies of design, production, consumption, use, and reuse.